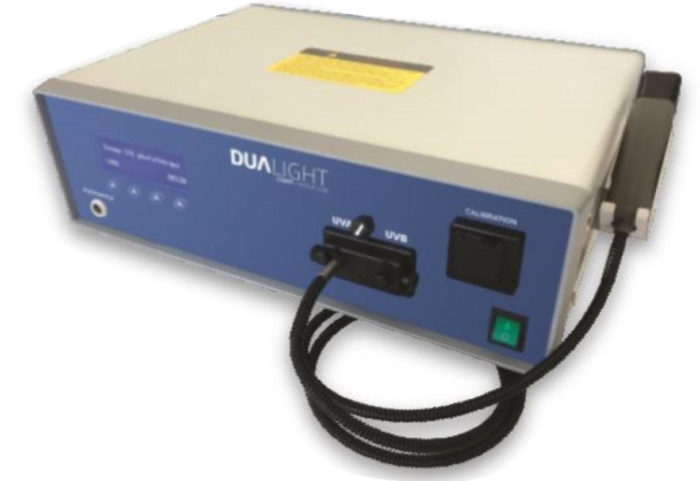
FDA Approved Targeted Narrow Band UV-B and UV-A PUVA Phototherapy For the in-office treatment of Psoriasis, Vitiligo and Eczema

Do you give 50% of your treatment revenue to your excimer laser company?
Do you pay $10,000 / year for excimer warranties and service?
Features
- FDA Approved
- Fully Reimbursed
- Manufactured in USA
- Both UV-B and UV-A (PUVA)
- Advanced Patented Treatment Handpiece
- Treats Psoriasis / Eczema / Vitiligo
- Safe and Simple Operation
- Color Touch Screen
- Compact and Portable
- Windows Based Controls
- No Maintenance Needed
- Photographic Lesion Documentation
- Automatic Patient Information Retrieval
- Preset Protocols and Digital Record Keeping
- Green Technology – No Gas Exchange Required
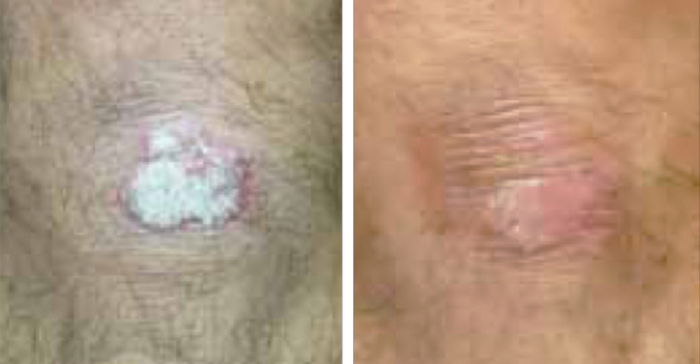
UV-B Phototherapy Psoriasis Before and After
UV-B Phototherapy Vitiligo Before and Afer
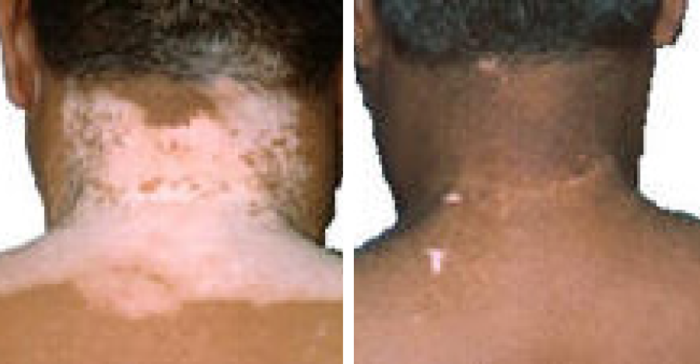
“We have used this system for four years. It is operated by my staff and the results are superior to Excimer. No maintenance is required and it has become a very profitable part of our practice.” David Vasily, MD – Bethlehem, PA
UV-B and UV-A (PUVA) Phototherapy
History and Discovery of Ultraviolet Radiation:
UV radiation was discovered in 1801 when the German physicist Johann Wilhelm Ritter conducted an experiment to investigate the existence of energy beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum. Knowing that photographic paper would turn black more rapidly in blue light than in red light, he exposed the paper to light beyond violet. The paper turned black, proving the existence of ultraviolet light. He called these invisible rays “(de-)oxidizing rays” to emphasize chemical reactivity and to distinguish them from “heat rays”, discovered the previous year at the other end of the visible spectrum. The simpler term “chemical rays” was adopted soon afterwards, and remained popular throughout the 19th century, although some said that this radiation was entirely different from light (notably John William Draper, who named them “tithonic rays”. The terms “chemical rays” and “heat rays” were eventually dropped in favor of ultraviolet and infrared radiation, respectively.
In 1878 the sterilizing effect of short-wavelength light by killing bacteria was discovered. By 1903 it was known the most effective wavelengths were around 250 nm. In 1960, the effect of ultraviolet radiation on DNA was established.
Modern phototherapy began with Nobel Prize winner Niels Finsen who developed a “chemical rays” lamp with which he treated patients with skin tuberculosis. However, it took several decades until phototherapy was introduced anew into the dermatological armamentarium. It was the development of photochemotherapy (PUVA) in 1974 that marked the beginning of a huge upsurge in Photodermatology.
In 1982, PUV-A therapy (the use of the photosensitizing drug Psoralen + UV-A), was approved by the FDA upon completion of one the largest clinical studies in the history of dermatology, a 1380 patient, (16) medical center trial led by the Massachusetts General Hospital and fifteen other major clinical centers around the country.
In the early 1990’s, another advance, Narrowband UV-B phototherapy, was introduced. Narrowband UV-B use has since become predominant because it uses a specific, narrow, spectrum of energy that has been clinically shown to be maximally effective.
How Does DuaLight UV-A & UV-B Phototherapy Work?
1. Power is applied to the DuaLight ionizing chamber
2. An Electrical Arc is generated from ionized gas which conducts electricity
3. Current is limited from the power source to protect the lamp and wiring
4. As arc temperature rises – mercury in the lamp converts to gaseous vapor state
5. Mercury vapor conducts electricity completing the circuit
6. UV output depends on the amount of mercury and vapor pressure
Treating Psoriasis:
Psoriasis results from an overactive immune response in the patient’s skin. Stimulation of T regulatory (T-reg) cells results in the downregulation of the overreactive immune response in psoriasis. UV radiation affects antigen presenting cells as well. After 3 – 5 UV treatments, the number of Langerhans cells is decreased by 90%, which alters overactive antigens. The photo-oxidative stress causes cytoskeleton damage in the remaining dendritic cells, which inhibits the further stimulation of T-cells. Cytokine secretion, as well as the number of macrophages, were also diminished by UV radiation. Through the action of the reactive oxygen species UV light switches off the activity of neutrophils and inhibits the natural killer (NK) cell function as well.
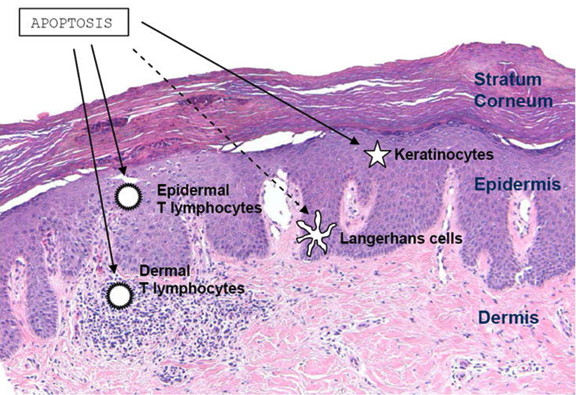
These cellular effects are accompanied by suppression of inflammatory cytokines IL-2, IL-8, IL-9, IL-17, IL-22 and IL-23, TNF-a and IFN-g, and induction of the immunosuppressive cytokine IL-10 also contributes to the cessation of psoriatic inflammation.
Summary of The Mechanism of Action and Effects of UV-B:
• UV-B radiation is absorbed by DNA and urocanic acid
• Alteration of cytokine profile
• Induction of apoptosis
• Promotion of immunosuppression
• Alters antigen-presenting cell activity
• Lowers peripheral natural killer (NK) cell activity, lymphocyte proliferation and immunoregulatory cytokine production by Th1 (IL-2, IFN-alpha) and Th2 (IL-10) T-cell populations
• UV-B results in erythema which begins 2 – 6 hours after exposure and peaks at 12 -18 hours after exposure generally lasting for 48 hours

SUMMARY:
Phototherapy is most efficacious treatment option for psoriasis. Current studies define the biological mechanisms by which phototherapy improves active psoriasis. Phototherapy works thru a combination of pathways to provide therapeutic benefits in treating this cutaneous disease.
